Advent of Code 2025 Day 9: Movie Theater
"""Advent of Code 2025: Day 9 - Movie Theater"""
from advent import parse, ints, combinations, defaultdict
def area(edge) -> int:
((x1, y1), (x2, y2)) = edge
return (abs(x2 - x1) + 1) * (abs(y2 - y1) + 1)
input = list(parse(9, ints))
pairs = sorted(combinations(input, 2), key=area, reverse=True)
edges = list(zip(input, input[1:] + [input[0]]))
def add_outside_border(edges, outside) -> None:
"""Walk the border of the polygon, and for every point,
add one to the right to represent the outside."""
for edge in edges:
((x1, y1), (x2, y2)) = edge
hdelta = x2 - x1
vdelta = y2 - y1
if abs(hdelta) == 0:
if vdelta > 0:
for y in range(y1, y2 + 1):
outside[x1 + 1].add(y)
else:
for y in range(y2, y1 + 1):
outside[x1 - 1].add(y)
else:
if hdelta > 0:
for x in range(x1, x2 + 1):
outside[x].add(y1 - 1)
else:
for x in range(x2, x1 + 1):
outside[x].add(y1 + 1)
def remove_poly_border(edges, outside) -> None:
"""Walk the border of the polygon, and remove every
point that was erroneously added to the outside dict."""
for edge in edges:
((x1, y1), (x2, y2)) = edge
hdelta = x2 - x1
vdelta = y2 - y1
if abs(hdelta) == 0:
if vdelta > 0:
for y in range(y1, y2 + 1):
outside[x1].discard(y)
else:
for y in range(y2, y1 + 1):
outside[x1].discard(y)
else:
if hdelta > 0:
for x in range(x1, x2 + 1):
outside[x].discard(y1)
else:
for x in range(x2, x1 + 1):
outside[x].discard(y1)
def is_valid(x1, y1, x2, y2, outside) -> bool:
"""Indicate whether the rectangle is valid by checking if any
outside points exist between y1 & y2 for every x coordinate."""
miny, maxy = min(y1, y2), max(y1, y2)
for x in range(min(x1, x2), max(x1, x2) + 1):
for y in outside[x]:
if miny <= y <= maxy:
return False
return True
def solve(is_valid):
"""Return the area of the first valid rectangle,
since we're checking in descending order by size."""
outside = defaultdict(set)
add_outside_border(edges, outside)
remove_poly_border(edges, outside)
for (x1, y1), (x2, y2) in pairs:
if is_valid(x1, y1, x2, y2, outside):
return (abs(x2 - x1) + 1) * (abs(y2 - y1) + 1)
assert solve(lambda *_: True) == 4737096935
assert solve(is_valid) == 1644094530
Input Parsing
The input format is simple today, but the parsing has some complexity to it. First, we'll
read the input as a list of 2-tuple ints into input. Second, we'll form all 2-element
combinations of those coordinates, and sort by the area represented by the two diagonal
points in descending order, and store in pairs. Lastly, we'll form a list of edges by
zipping.
def area(edge) -> int:
((x1, y1), (x2, y2)) = edge
return (abs(x2 - x1) + 1) * (abs(y2 - y1) + 1)
input = list(parse(9, ints))
pairs = sorted(combinations(input, 2), key=area, reverse=True)
edges = list(zip(input, input[1:] + [input[0]]))
Solution
Today was relatively difficult, but I was determined to solve it without help if possible. I came up with a cumbersome algorithm that worked, before discovering a Python library that made a very elegant solution (see below). My algorithm was to "walk" the polygon, and for each point on the polygon, add the point to my right to indicate "outside". I first checked that both the sample and real inputs describe a polygon in counter-clockwise fashion.
Unfortunately, this process also marked some points directly on the polygon as "outside" erroneously, so I made a second pass to fix those issues.
With the hard work done, I iterate over the rectangles in pairs, and return the area of
the first valid one. This produces the correct answer because pairs is in order from the largest
to the smallest.
The is_valid helper function iterates over the columns of the rectangle, and checks to see
if any of the points in the outside set are within the column. After I posted my solution,
I realized from some hints that I could skip my home grown "outside" border solution, and just
checked for intersections between the polygon and my candidate rectangle.
The same solve function produces answers to both parts by using a
higher order function for each part. For part 1, all rectangles are valid, and for
part 2 the is_valid function is used as the predicate.
Using Shapely
Scott Moonen mentioned the shapely library for Python, so I created the following part 2 solution with it.
The polygon.contains() function made it trivial:
"""Advent of Code 2025: Day 9 - Movie Theater (using shapely)"""
from advent import parse, ints, combinations
from shapely.geometry import Polygon, box
def part2():
def area(edge) -> int:
((x1, y1), (x2, y2)) = edge
return (abs(x2 - x1) + 1) * (abs(y2 - y1) + 1)
input = parse(9, ints)
polygon = Polygon(input)
for edge in sorted(combinations(input, 2), key=area, reverse=True):
(x1, y1), (x2, y2) = edge
if polygon.contains(box(x1, y1, x2, y2)):
return area(edge)
assert part2() == 1644094530
Visualization
Before tackling the problem, I wanted to get an idea of what the input looked like visually. Here's my input:
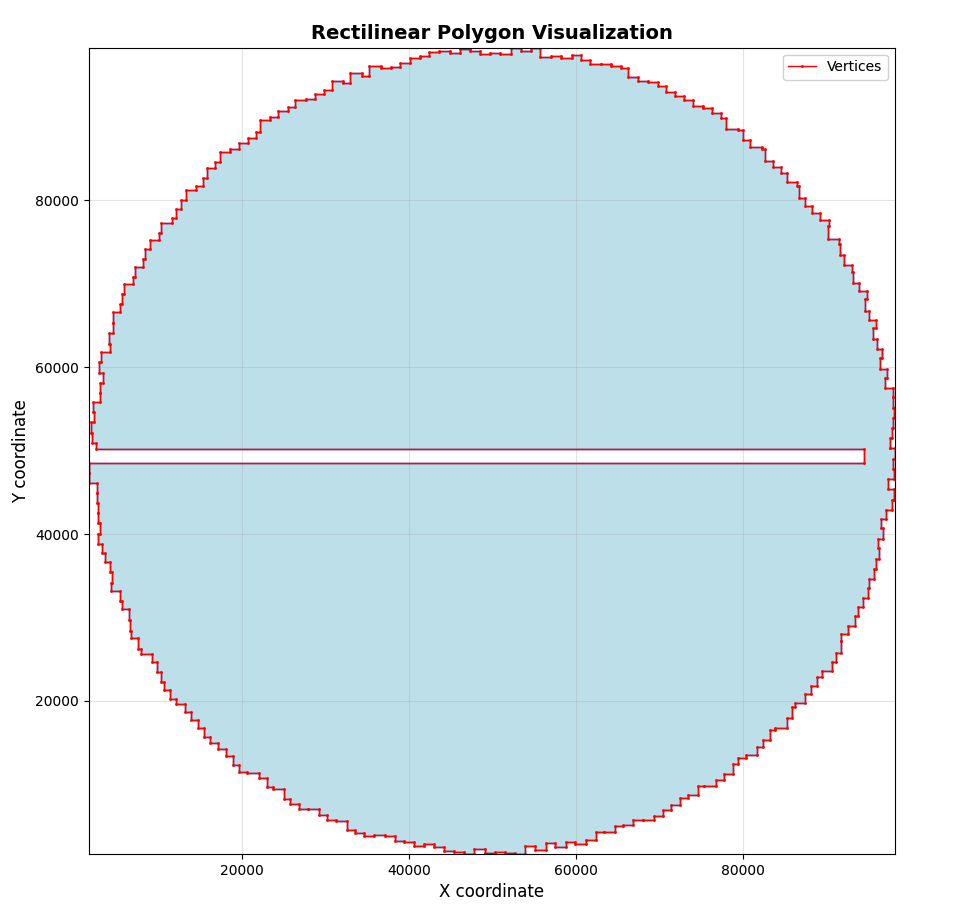
Produced by this Python code:
from advent import parse, ints, plt
from matplotlib.patches import Polygon
vertices = parse(9, ints)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
polygon = Polygon(
vertices, fill=True, facecolor='lightblue', edgecolor='darkblue', linewidth=1, alpha=0.7
)
ax.add_patch(polygon)
x_coords, y_coords = zip(*vertices)
ax.plot(
x_coords + (x_coords[0],),
y_coords + (y_coords[0],),
'ro-',
markersize=1,
linewidth=1,
label='Vertices',
)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xlabel('X coordinate', fontsize=12)
ax.set_ylabel('Y coordinate', fontsize=12)
ax.set_title('Rectilinear Polygon Visualization', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax.legend()
margin = 0.5
all_x = [v[0] for v in vertices]
all_y = [v[1] for v in vertices]
ax.set_xlim(min(all_x) - margin, max(all_x) + margin)
ax.set_ylim(min(all_y) - margin, max(all_y) + margin)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()